Tubal Ligation: Empowering Women’s Reproductive Choice and Family Planning
Introduction
Tubal ligation, also known as “getting your tubes tied,” is a permanent form of female sterilization. It is a popular method of contraception for women who have completed their desired family size or have chosen not to have children. In this blog, we will explore tubal ligation, its procedure, considerations, benefits, and the impact it has on women’s reproductive autonomy.
Understanding Tubal Ligation
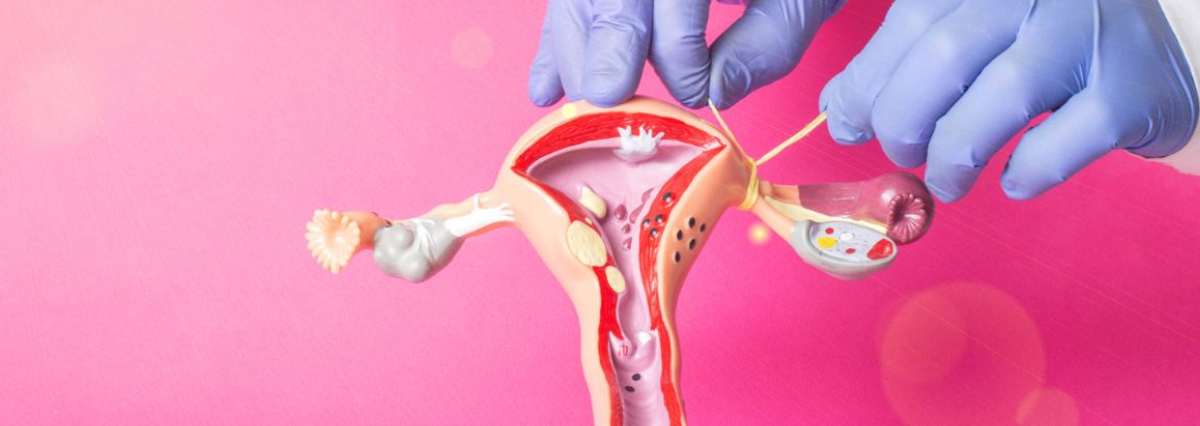
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes, which prevents eggs from reaching the uterus and sperm from reaching the eggs. The procedure can be performed through various techniques, including laparoscopy, mini-laparotomy, or hysteroscopy. It is typically an outpatient procedure that offers a high success rate in preventing pregnancy. Tubal ligation is considered a permanent method of contraception, and its effects are irreversible, so it is important for women to carefully consider their reproductive goals before opting for this procedure.
Procedure and Recovery
Tubal ligation is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation, depending on the technique used. Laparoscopic tubal ligation involves making small incisions in the abdomen, inserting a laparoscope, and using specialized instruments to seal or block the fallopian tubes. Mini-laparotomy involves a small incision near the navel to access the tubes for sealing. Hysteroscopic tubal ligation is a non-surgical procedure that involves placing small devices or coils inside the fallopian tubes through the vagina and cervix. Recovery time varies, but most women can resume their normal activities within a few days to a week.
Considerations and Benefits
Tubal ligation offers several advantages for women who have decided to pursue permanent contraception. It provides a reliable method of birth control without the need for ongoing contraception, such as taking hormonal pills or using barrier methods. It allows women to have control over their reproductive choices, enabling them to focus on other aspects of their lives and make decisions based on their individual circumstances. Tubal ligation does not affect hormonal balance, menstruation, or sexual functioning. However, it is important to note that tubal ligation does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and if there is a chance of reconsidering future fertility, alternative contraception options should be explored.
Counseling and Informed Decision-Making
Before undergoing tubal ligation, women should receive comprehensive counseling from healthcare professionals. This includes discussions about the permanence of the procedure, potential risks and complications, alternative contraception methods, and the importance of ensuring that the individual is fully informed and confident in their decision. Healthcare providers should respect women’s autonomy and support their reproductive choices, providing non-judgmental guidance and ensuring they have access to accurate information.
Conclusion
Tubal ligation offers a permanent and effective form of contraception for women who have made the decision to no longer pursue pregnancy. By providing control over reproductive choices, tubal ligation empowers women to shape their lives according to their desires and circumstances. With proper counseling, informed decision-making, and support from healthcare professionals, women can confidently embrace the freedom that tubal ligation provides in their reproductive journey.
